鉴赏 Compute Shader #1
您更新了 9 分钟前 • 评论 • 被浏览 仅您自己
前言
本文收集有意思的 Compute Shader 效果,给源码配上注释以及自己的理解
BufferJoy
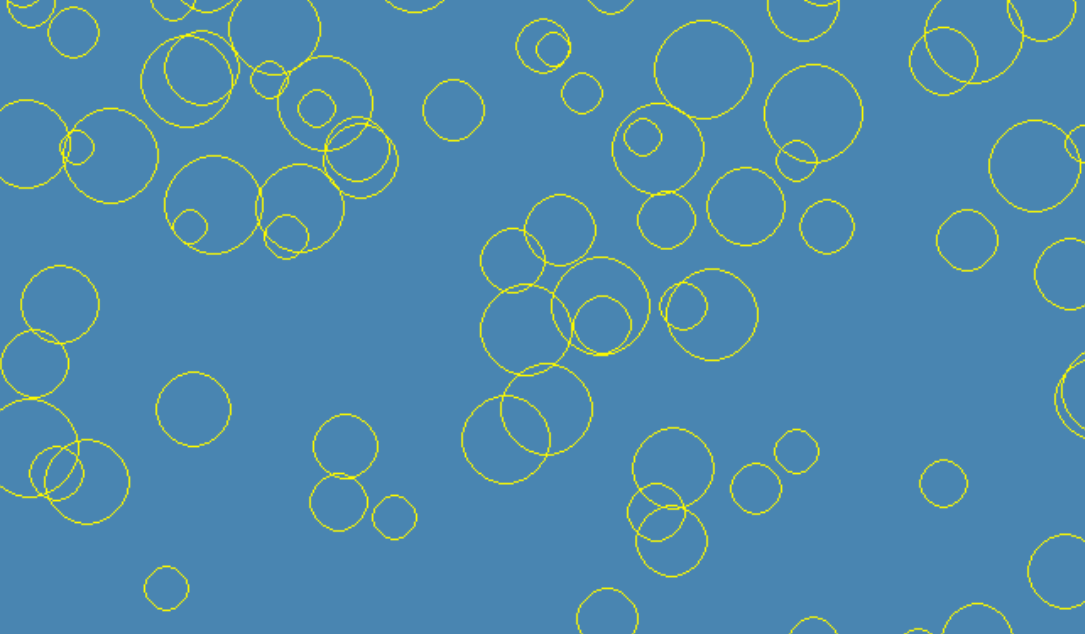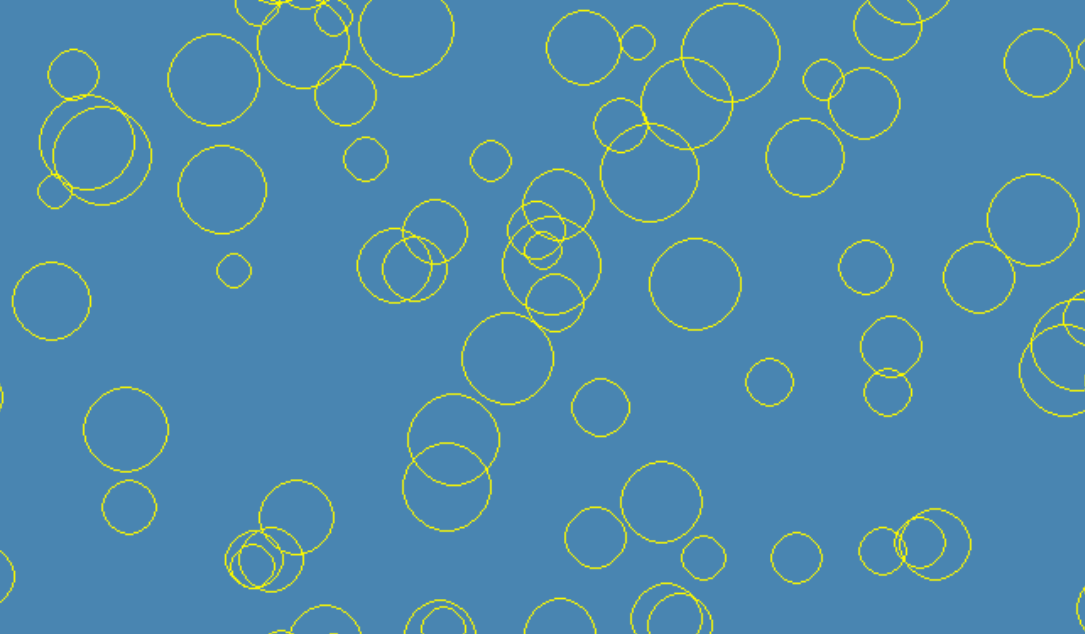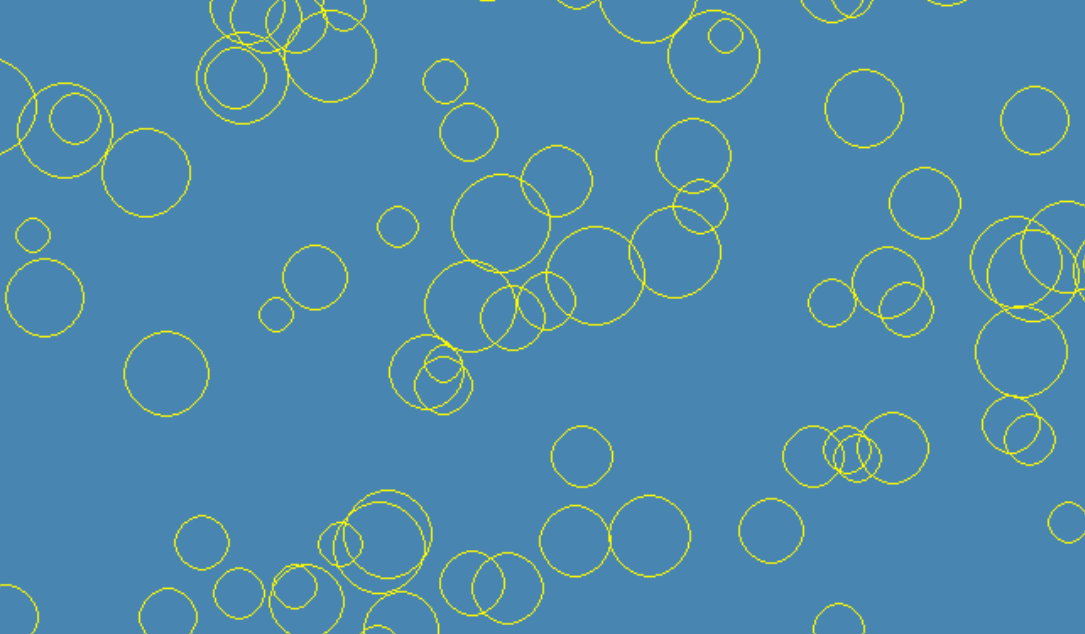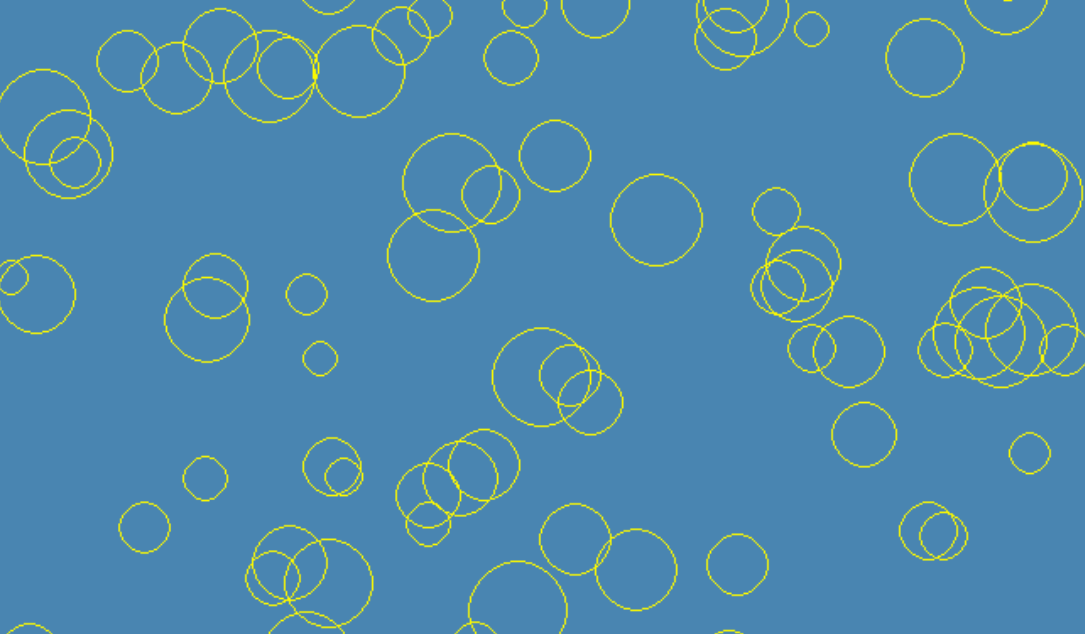
//关键代码
public class BufferJoy : MonoBehaviour
{
...
struct Circle
{
public Vector2 origin;
public Vector2 velocity;
public float radius;
}
int count = 10;
Circle[] circleData;
ComputeBuffer buffer;
// Use this for initialization
void Start()
{
outputTexture = new RenderTexture(texResolution, texResolution, 0);
outputTexture.enableRandomWrite = true;
outputTexture.Create();
rend = GetComponent<Renderer>();
rend.enabled = true; //这一步是必要的,否则不能读写
InitData();
InitShader();
}
private void InitData()
{
circlesHandle = shader.FindKernel("Circles");
uint threadGroupSizeX;
shader.GetKernelThreadGroupSizes(circlesHandle, out threadGroupSizeX, out _, out _);
int total = (int)threadGroupSizeX * count;
circleData = new Circle[total];
//以下省略对circleData随机赋值
}
private void InitShader()
{
clearHandle = shader.FindKernel("Clear");
shader.SetVector( "clearColor", clearColor );
shader.SetVector( "circleColor", circleColor );
shader.SetInt( "texResolution", texResolution );
int stride = (2 + 2 + 1) * 4; //2 floats origin, 2 floats velocity, 1 float radius - 4 bytes per float
buffer = new ComputeBuffer(circleData.Length, stride);
buffer.SetData(circleData);
//SetBuffer需要指定kernelHandle,因为一个计算着色器可以包含多个核心,每个核心可能需要不同的输入或输出缓冲区。
shader.SetBuffer(circlesHandle, "circlesBuffer", buffer); //传递buffer
shader.SetTexture( circlesHandle, "Result", outputTexture );
shader.SetTexture( clearHandle, "Result", outputTexture );
rend.material.SetTexture("_MainTex", outputTexture);
}
private void DispatchKernel(int count)
{
shader.Dispatch(clearHandle, texResolution/8, texResolution/8, 1); //删除上一帧
shader.SetFloat("time", Time.time); //设置随时间变化
//shader.SetBool("clearScreen", true );
shader.Dispatch(circlesHandle, count, 1, 1); //绘图
}
void Update()
{
DispatchKernel(10); //总共32x10=320个圆,[numthreads(32,1,1)]
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
buffer.Dispose();
}
}//Compute Shader实现
#pragma kernel Circles
#pragma kernel Clear
shared RWTexture2D<float4> Result;
struct circle
{
float2 origin;
float2 velocity;
float radius;
}; //对应cs中 struct Circle
StructuredBuffer<circle> circlesBuffer; //用于传递buffer
float4 clearColor;
float4 circleColor;
int texResolution;
int clearScreen = 0;
float time;
//伪随机数序列,范围0 <= x < 1
float random(float value, float seed = 0.546){
float random = (frac(sin(value + seed) * 143758.5453));// + 1.0)/2.0;
return random;
}
//生成伪随机二维向量
float2 random2(float value){
return float2(
random(value, 3.9812),
random(value, 7.1536)
);
}
//Result以位置为索引,值为对应的颜色,这是在给对应的位置涂色
void plot1( int x, int y, int2 centre){
Result[uint2(centre.x + x, centre.y + y)] = circleColor;
}
//用于绘制圆上的八个点,实现八分对称的绘制
//可以实现更快速的圆形绘制,因为每个点只需要计算一次,然后根据对称性在其他位置上复制。
void plot8( int x, int y, int2 centre ) {
plot1( x, y, centre ); plot1( y, x, centre );
plot1( x, -y, centre ); plot1( y, -x, centre );
plot1( -x, -y, centre ); plot1( -y, -x, centre );
plot1( -x, y, centre ); plot1( -y, x, centre );
}
//使用了 Bresenham 圆形绘制算法的变体
//在每一步迭代中,根据当前点的位置和距离圆形边界的距离,确定下一个点的位置,
//并根据对称性在圆形的八个对称位置上绘制点。
void drawCircle( int2 centre, int radius){
int x = 0;
int y = radius;
int d = 1 - radius;
while (x < y){
if (d < 0){
d += 2 * x + 3;
}else{
d += 2 * (x - y) + 5;
y--;
}
plot8(x, y, centre);
x++;
}
}
[numthreads(32,1,1)]
void Circles (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
int2 centre = (int2)(circlesBuffer[id.x].origin + circlesBuffer[id.x].velocity * time);
//偏移圆的位置以将其限制在纹理范围内
while (centre.x>texResolution) centre.x -= texResolution;
while (centre.x<0) centre.x += texResolution;
while (centre.y>texResolution) centre.y -= texResolution;
while (centre.y<0) centre.y += texResolution;
uint radius = (int)circlesBuffer[id.x].radius;
//以上数据都从cs中的SetBuffer函数中获取了
drawCircle( centre, radius );
}
[numthreads(8,8,1)]
void Clear (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
Result[id.xy] = clearColor;
}FishStorm
.gif)
public class FishStorm: MonoBehaviour
{
public struct Boid
{
public Vector3 position;
public Vector3 direction;
public float noise_offset;
public float theta;
public Boid(Vector3 pos, Vector3 dir, float offset)
{
position.x = pos.x;
position.y = pos.y;
position.z = pos.z;
direction.x = dir.x;
direction.y = dir.y;
direction.z = dir.z;
noise_offset = offset;
theta = Random.value * Mathf.PI * 2;
}
}
void Start()
{
//...省略计算线程组数等操作
InitBoids();
InitShader();
}
private void InitBoids()
{
boids = new GameObject[numOfBoids];
boidsArray = new Boid[numOfBoids];
//全局变量 int numOfBoids;
for (int i = 0; i < numOfBoids; i++)
{
//很聪明的设置随机出生范围的方法,Random.insideUnitSphere * spawnRadius;
Vector3 pos = transform.position + Random.insideUnitSphere * spawnRadius;
//随机旋转
Quaternion rot = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Random.rotation, 0.3f);
float offset = Random.value * 1000.0f;
boidsArray[i] = new Boid(pos, rot.eulerAngles, offset);
}
}
void InitShader()
{
boidsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(numOfBoids, 8 * sizeof(float));
boidsBuffer.SetData(boidsArray);
//全局变量 ComputeBuffer argsBuffer; Mesh boidMesh;
//uint[] args = new uint[5] { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; int numOfBoids;
argsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments);
if (boidMesh != null)
{
//获取网格中子网格索引数组中指定子网格的索引数,返回的是指定子网格中的三角形索引的数量
//0:对于大多数网格来说,它们只有一个子网格,因此参数通常设置为 0
args[0] = (uint)boidMesh.GetIndexCount(0);
args[1] = (uint)numOfBoids;
}
argsBuffer.SetData(args);
shader.SetBuffer(this.kernelHandle, "boidsBuffer", boidsBuffer);
shader.SetFloat("rotationSpeed", rotationSpeed);
shader.SetFloat("boidSpeed", boidSpeed);
shader.SetFloat("boidSpeedVariation", boidSpeedVariation);
shader.SetVector("flockPosition", target.transform.position);
shader.SetFloat("neighbourDistance", neighbourDistance);
shader.SetInt("boidsCount", numOfBoids);
//全局变量 public Material boidMaterial;
//通常情况下,我们会使用 shader.SetBuffer 来设置 Compute Shader 中的缓冲区。
//使用 Material 的 SetBuffer 方法通常是在需要将缓冲区数据传递给 GPU 进行渲染的情况下,
//例如,当你想在顶点或片段着色器中访问缓冲区数据时。
//在某些情况下,使用 Material 的 SetBuffer 方法可能更方便,特别是当你已经在着色器中使用了该 Material,并且想要在渲染特定的对象时使用缓冲区数据时。
boidMaterial.SetBuffer("boidsBuffer", boidsBuffer);
}
void Update()
{
shader.SetFloat("time", Time.time);
shader.SetFloat("deltaTime", Time.deltaTime);
shader.Dispatch(this.kernelHandle, groupSizeX, 1, 1);
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect(boidMesh, 0, boidMaterial, bounds, argsBuffer, 0, props);
}
void OnDestroy()
{
//Dispose Buffers ....
}
}#pragma kernel CSMain
#define GROUP_SIZE 256
#define PI2 6.28318530718
//一个简单的哈希算法
float hash( float n )
{
return frac(sin(n)*43758.5453);
}
// The noise function returns a value in the range -1.0f -> 1.0f
float noise1( float3 x )
{
float3 p = floor(x);
float3 f = frac(x);
f = f*f*(3.0-2.0*f);
float n = p.x + p.y*57.0 + 113.0*p.z;
return lerp(lerp(lerp( hash(n+0.0), hash(n+1.0),f.x),
lerp( hash(n+57.0), hash(n+58.0),f.x),f.y),
lerp(lerp( hash(n+113.0), hash(n+114.0),f.x),
lerp( hash(n+170.0), hash(n+171.0),f.x),f.y),f.z);
}
struct Boid
{
float3 position;
float3 direction;
float noise_offset;
float theta;
};
RWStructuredBuffer<Boid> boidsBuffer;
float time;
float deltaTime;
float rotationSpeed;
float boidSpeed;
float boidSpeedVariation;
float3 flockPosition;
float neighbourDistance;
int boidsCount;
[numthreads(GROUP_SIZE,1,1)]
void CSMain (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint instanceId = id.x;
Boid boid = boidsBuffer[instanceId];
//生成噪声
float noise = clamp(noise1(time / 100.0 + boid.noise_offset), -1, 1) * 2.0 - 1.0;
float velocity = boidSpeed * (1.0 + noise * boidSpeedVariation); //这个例子中boidSpeedVariation设置为1
//用于计算两个数相除的余数
boid.theta = fmod(boid.theta + deltaTime * 4, PI2);
float3 boid_pos = boid.position;
float3 boid_dir = boid.direction;
float3 separation = 0;
float3 alignment = 0;
float3 cohesion = flockPosition; //target.transform.position,target为群体中心,提前设定好的
uint nearbyCount = 1; // Add self that is ignored in loop
//循环计算附近其他 boids 对当前 boid 的影响
for (uint i = 0; i < (uint)boidsCount; i++) {
if (i == instanceId)
continue;
if (distance(boid_pos, boidsBuffer[i].position) < neighbourDistance)
{
float3 tempBoid_position = boidsBuffer[i].position;
float3 diff = boid_pos - tempBoid_position;
float diffLen = (length(diff));
float scaler = clamp(1.0 - diffLen / neighbourDistance, 0.0, 1.0);
separation += diff * (scaler / diffLen);
alignment += boidsBuffer[i].direction;
cohesion += tempBoid_position;
nearbyCount += 1;
}
}
//加上群体影响,更新位置和方向
float avg = 1.0 / nearbyCount;
alignment *= avg;
cohesion *= avg;
cohesion = normalize(cohesion - boid_pos);
float3 direction = alignment + separation + cohesion;
float ip = exp(-rotationSpeed * deltaTime);
boid.direction = lerp((direction), normalize(boid_dir), ip);
boid.position += (boid.direction) * (velocity * deltaTime);
boidsBuffer[id.x] = boid;
}


