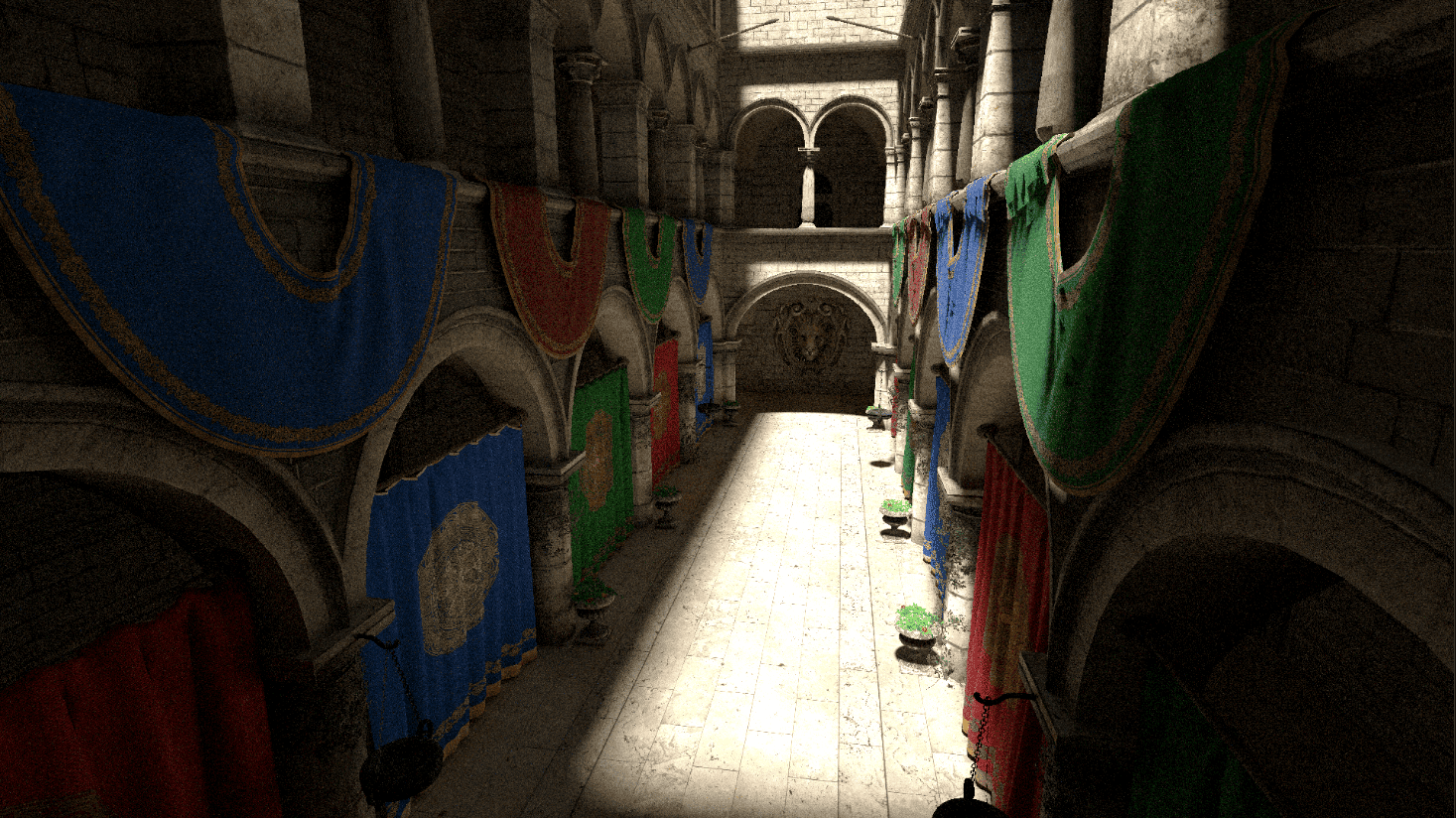
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
省略启发式AABB构建过程....
SDF形状实现
基类:
[ExecuteInEditMode]
public class RayMarchedShape : MonoBehaviour
{
private static AabbTree<RayMarchedShape> s_tree = new AabbTree<RayMarchedShape>();
private static List<RayMarchedShape> s_shapeComponents = new List<RayMarchedShape>();
private static List<SdfShape> s_sdfShapes = new List<SdfShape>();
public static List<SdfShape> GetShapes()
{
if (s_sdfShapes.Capacity < s_shapeComponents.Count)
{
s_sdfShapes.Capacity = s_shapeComponents.Count;
}
s_sdfShapes.Clear();
foreach (var s in s_shapeComponents)
{
var sdfShape = s.Shape;
sdfShape.Operator = (int) s.Operator;
s_sdfShapes.Add(sdfShape);
}
return s_sdfShapes;
}s_shapeComponents:存放场景中所有启用的 RayMarchedShape 实例。
s_tree:对应的 AABB 树结构,用于快速做空间剔除和射线相交测试。
s_sdfShapes:每帧根据组件列表生成的 SdfShape 数组,降低运行时的内存分配和 GC 频率,逻辑上不是必须。
private int m_shapeIndex = -1;
private int m_iProxy = AabbTree<RayMarchedShape>.Null;
private void OnEnable()
{
// 1. 插入全局列表
m_shapeIndex = s_shapeComponents.Count;
s_shapeComponents.Add(this);
// 2. 在 BVH 树里为自己创建一个 proxy 节点
m_iProxy = s_tree.CreateProxy(Bounds, this);
}
private void OnDisable()
{
// 1. 从列表中移除,并把最后一个元素“填补”到当前位置
s_shapeComponents[m_shapeIndex] = s_shapeComponents[s_shapeComponents.Count - 1];
s_shapeComponents[m_shapeIndex].m_shapeIndex = m_shapeIndex;
s_shapeComponents.RemoveAt(s_shapeComponents.Count - 1);
m_shapeIndex = -1;
// 2. 销毁 BVH 树里的 proxy
s_tree.DestroyProxy(m_iProxy);
m_iProxy = AabbTree<RayMarchedShape>.Null;
}OnEnable:每当一个带 RayMarchedShape 的 GameObject 激活时,就把它加入 s_shapeComponents,并在 s_tree 中开辟一个 proxy,用它来跟踪该物体的包围盒(Bounds)。
OnDisable:移除列表和 BVH proxy。同样保证列表紧凑,无“空洞”。
public static int FillAabbTree(ComputeBuffer buffer, float aabbTightenRadius = 0.0f)
{
SyncBounds(); // 更新所有 proxy 的包围盒位置/大小
int root = s_tree.Fill(buffer, aabbTightenRadius);
return root;
}
public static void SyncBounds()
{
foreach (var s in s_shapeComponents)
s_tree.UpdateProxy(s.m_iProxy, s.Bounds);
}SyncBounds:把每个组件最新的 Bounds(由子类 override)写入对应的 proxy。
Fill:让 AABB 树重建内部节点,并把树的数据打平写入到 GPU 用的 ComputeBuffer。
返回值 root 是根节点在数组中的下标,也会传给 GPU Shader,用来做递归遍历。
球类(继承类):
[ExecuteInEditMode]
public class RayMarchedSphere : RayMarchedShape
{
public float Radius = 0.5f;
protected override SdfShape Shape
{
get
{
return SdfShape.Sphere(transform.position, Radius);
}
}
public override Aabb Bounds
{
get
{
return
new Aabb
(
transform.position - Radius * Vector3.one,
transform.position + Radius * Vector3.one
);
}
}
protected override void OnValidate()
{
base.OnValidate();
Radius = Mathf.Max(0.0f, Radius);
}
}球的AABB包围盒的求法很简单,符合直觉
SDF形状:
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 0)]
public struct SdfShape
{
public static readonly int Stride = 4 * sizeof(int) + 12 * sizeof(float);
public enum TypeEnum
{
Sphere,
Box,
Capsule,
Cylinder,
}
public int Type;
public int Operator;
public int Padding1;
public int Padding2;
public Vector4 Data0;
public Vector4 Data1;
public Vector4 Data2;
private static void WarningSuppression()
{
SdfShape shape;
shape.Type = shape.Padding2 = 0;
shape.Padding2 = shape.Type = 0;
}
public static SdfShape Dummy()
{
SdfShape shape;
shape.Type = 0;
shape.Operator = 0;
shape.Padding1 = 0;
shape.Padding2 = 0;
shape.Data0 = Vector4.zero;
shape.Data1 = Vector4.zero;
shape.Data2 = Vector4.zero;
return shape;
}
public static SdfShape Sphere(Vector3 center, float radius)
{
SdfShape shape;
shape.Type = 0;
shape.Operator = shape.Padding1 = shape.Padding2 = 0;
shape.Data0 = new Vector4(center.x, center.y, center.z, radius);
shape.Data1 = Vector4.zero;
shape.Data2 = Vector4.zero;
return shape;
}
public static SdfShape Box(Vector3 center, Vector3 halfExtents, Quaternion rotation, float radius = 0.0f)
{
SdfShape shape;
shape.Type = 1;
shape.Operator = shape.Padding1 = shape.Padding2 = 0;
shape.Data0 = new Vector4(center.x, center.y, center.z, radius);
shape.Data1 = new Vector4(halfExtents.x, halfExtents.y, halfExtents.z);
shape.Data2 = new Vector4(rotation.x, rotation.y, rotation.z, rotation.w);
return shape;
}
public static SdfShape Capsule(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, float radius)
{
SdfShape shape;
shape.Type = 2;
shape.Operator = shape.Padding1 = shape.Padding2 = 0;
shape.Data0 = new Vector4(a.x, a.y, a.z, radius);
shape.Data1 = new Vector4(b.x, b.y, b.z);
shape.Data2 = Vector4.zero;
return shape;
}
public static SdfShape Cylinder(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, float radius)
{
SdfShape shape;
shape.Type = 3;
shape.Operator = shape.Padding1 = shape.Padding2 = 0;
shape.Data0 = new Vector4(a.x, a.y, a.z, radius);
shape.Data1 = new Vector4(b.x, b.y, b.z);
shape.Data2 = Vector4.zero;
return shape;
}
}RayMarching 后处理 ComputeShader
// cs
[Range(1, 256)]
public int MaxRaySteps = 128;
public float RayHitThreshold = 0.005f;
public float MaxRayDistance = 1000.0f;
compute.SetVector(m_const.RayMarchParams, new Vector4(MaxRaySteps, RayHitThreshold, MaxRayDistance, Time.time));
// compute shader
const int maxSteps = int(rayMarchParams.x);
const float hitDist = rayMarchParams.y;
const float maxDist = rayMarchParams.z;小tip
var window = EditorWindow.GetWindow<SceneView>(false, "", false);
var camera = window ? window.camera : null;可以获取Scene视图的相机,还真是万物皆可组件,Scene上也有Camera组件
求交
// gather shapes around ray by casting it against AABB tree
int nearShapes[kMaxShapesPerRay];
int numNearShapes = 0;
aabb_tree_ray_cast(aabbTree, aabbTreeRoot, ro, ro + maxDist * rd, kAabbTreeStackSize,
numNearShapes = min(numNearShapes + 1, kMaxShapesPerRay);
nearShapes[numNearShapes - 1] = shapeIndex;
);数量:numNearShapes 这是一个计数器,初始为 0。 索引列表:数组 aiNearShape(长度上限 kMaxShapesPerRay)用来存放「这条射线可能会命中的」那些 SDF 形状在全局 aSdfShape 数组里的 索引(shapeIndex)。数组下标范围是 0~numNearShapes-1,每次发现一个叶子 AABB 被射线击中,就把它对应的 shapeIndex push 进去。
March Ray
//对 numNearShapes 个候选形状做距离评估
#define SDF_NEAR_SHAPES(res, p, aiNearShape, numNearShapes) \
{ \
float3 opRes = kInfinity; \
for (int i = 0; i < numNearShapes; ++i) \
{ \
const int iShape = aiNearShape[i]; \
const int op = aSdfShape[iShape].data0.y; \
if (op == kSdfUnion) \
{ \
opRes.x = sdf_uni_smooth(opRes.x, sdf_shape(p, aSdfShape[iShape]), blendDist); \
} \
else if (op == kSdfSubtraction) \
{ \
opRes.y = sdf_uni_smooth(opRes.y, sdf_shape(p, aSdfShape[iShape]), blendDist); \
} \
else if (op == kSdfIntersection) \
{ \
opRes.z = sdf_uni_smooth(opRes.z, sdf_shape(p, aSdfShape[iShape]), blendDist); \
} \
} \
res = sdf_sub_smooth(opRes.x, opRes.y, blendDist); \
if (opRes.z < kInfinity) \
res = sdf_int_smooth(res, opRes.z, blendDist); \
}
// 主要逻辑
float dist = 0.0f;
// Ray Marching
for (int iStep = 0; iStep < maxSteps; ++iStep)
{
const float3 p = ro + dist * rd;
// sample SDf
float d = kInfinity;
SDF_NEAR_SHAPES(d, p, nearShapes, numNearShapes);
// hit shape?
if (d < hitDist)
{
if (mode == kModeMain)
{
const float h = 0.01f;
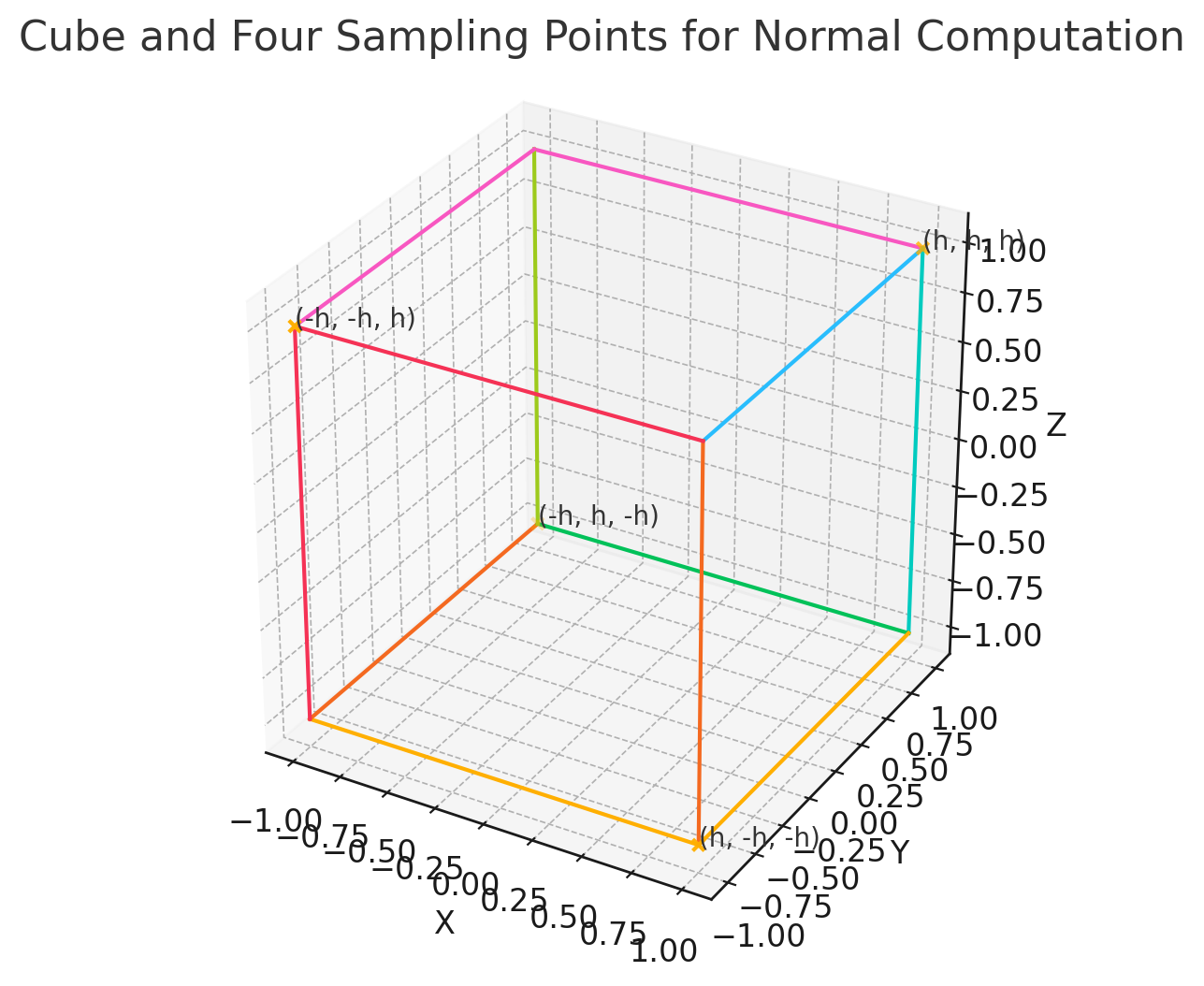
// compute differential normal
float3 n = 0.0f;
// 计算法线
float n0, n1, n2, n3;
SDF_NEAR_SHAPES(n0, p + float3( (h), -(h), -(h)), nearShapes, numNearShapes);
SDF_NEAR_SHAPES(n1, p + float3(-(h), -(h), (h)), nearShapes, numNearShapes);
SDF_NEAR_SHAPES(n2, p + float3(-(h), (h), -(h)), nearShapes, numNearShapes);
SDF_NEAR_SHAPES(n3, p + float3( (h), (h), (h)), nearShapes, numNearShapes);
n =
normalize
(
float3( 1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f) * n0
+ float3(-1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f) * n1
+ float3(-1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f) * n2
+ float3( 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f) * n3
);
const float3 lightPos = ro + float3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
const float3 lightDir = normalize(p - lightPos);
const float3 shaded = max(pow(dot(n, -lightDir), 1.0f), kAmbient) * kDiffuse;
const float3 fresnel = 0.3f * pow(saturate(1.0f - dot(n, -rd)), 2.0f);
const float3 specular = 0.2f * pow(saturate(dot(n, -normalize(rd + lightDir))), 100.0f);
return float4(shaded + fresnel + specular, d);
}
}
// hit background?
if (dist > maxDist)
{
return float4(backgroundColor.rgb, kInfinity);
}
dist += d;
}
if (mode != kModeMain)
return kInfinity;
return float4(missColor.rgb, kInfinity);
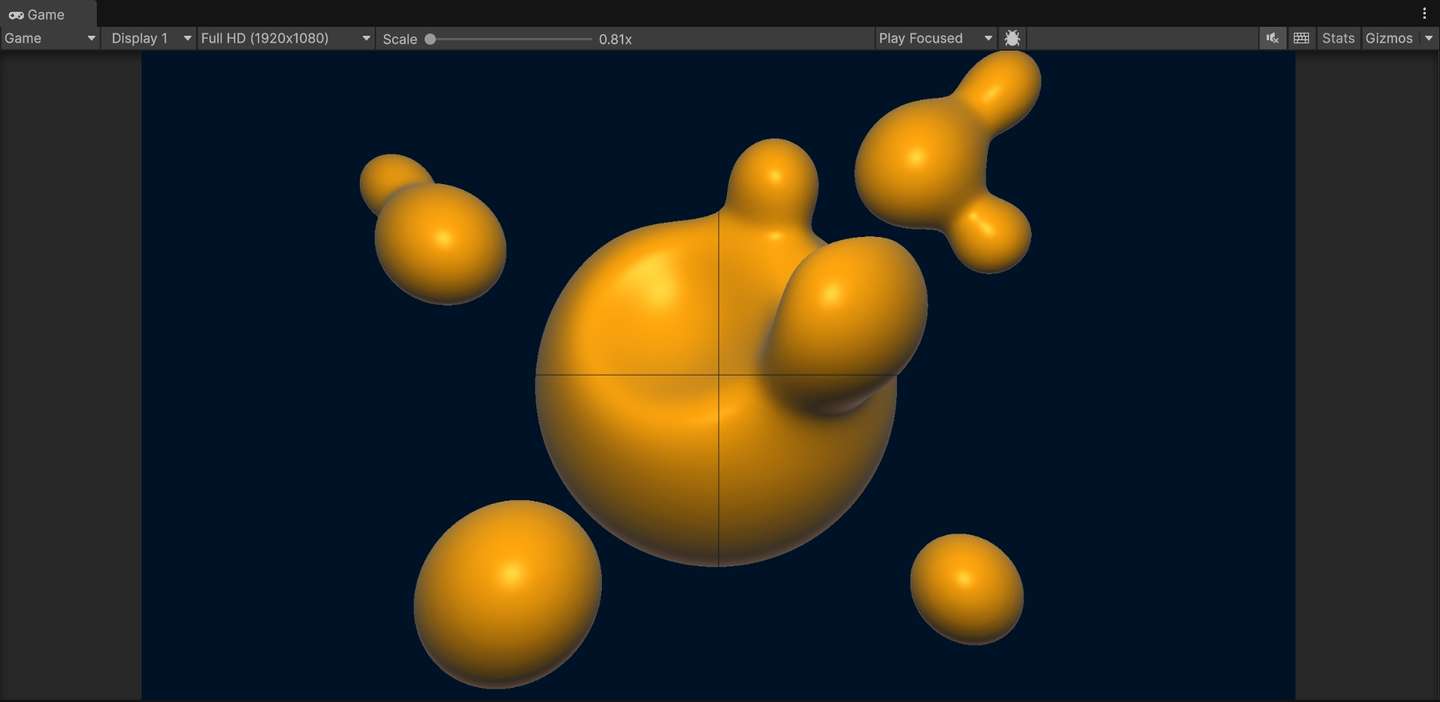
}这段代码没有严谨地考虑穿过的情况,也就是两个Step之间距离都小于hitDst的情况,但场景里都是球体,并没有厚度小于hitDst的平面。
看完这个代码我才知道原来SDF在渲染中的作用就是计算法线。
用立方体的四个对顶角计算,4 个点正好能提供三个自由度的梯度信息(∂x,∂y,∂z)加上一个整体偏移。
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Lerp 平滑
// 平滑并集(smooth union)
float sdf_uni_smooth(float a, float b, float k)
{
// h 从 0 到 1,表示 a,b 在过渡带中的插值权重
float h = saturate(0.5 + 0.5*(b - a)/k);
// 线性插值再减去一段抛物线以保证曲线光滑
return lerp(b, a, h) - k*h*(1.0 - h);
}
// 平滑差集(smooth subtraction)
float sdf_sub_smooth(float a, float b, float k)
{
// 先把 b 取反,再当成并集处理
return sdf_uni_smooth(a, -b, k);
}
// 平滑交集(smooth intersection)
float sdf_int_smooth(float a, float b, float k)
{
// 交集是 max(a,b),平滑版可以写成
float h = saturate(0.5 - 0.5*(b - a)/k);
return lerp(b, a, h) + k*h*(1.0 - h);
}对计算出的法线进行插值,形成一种平滑的Mesh效果

.jpg)

